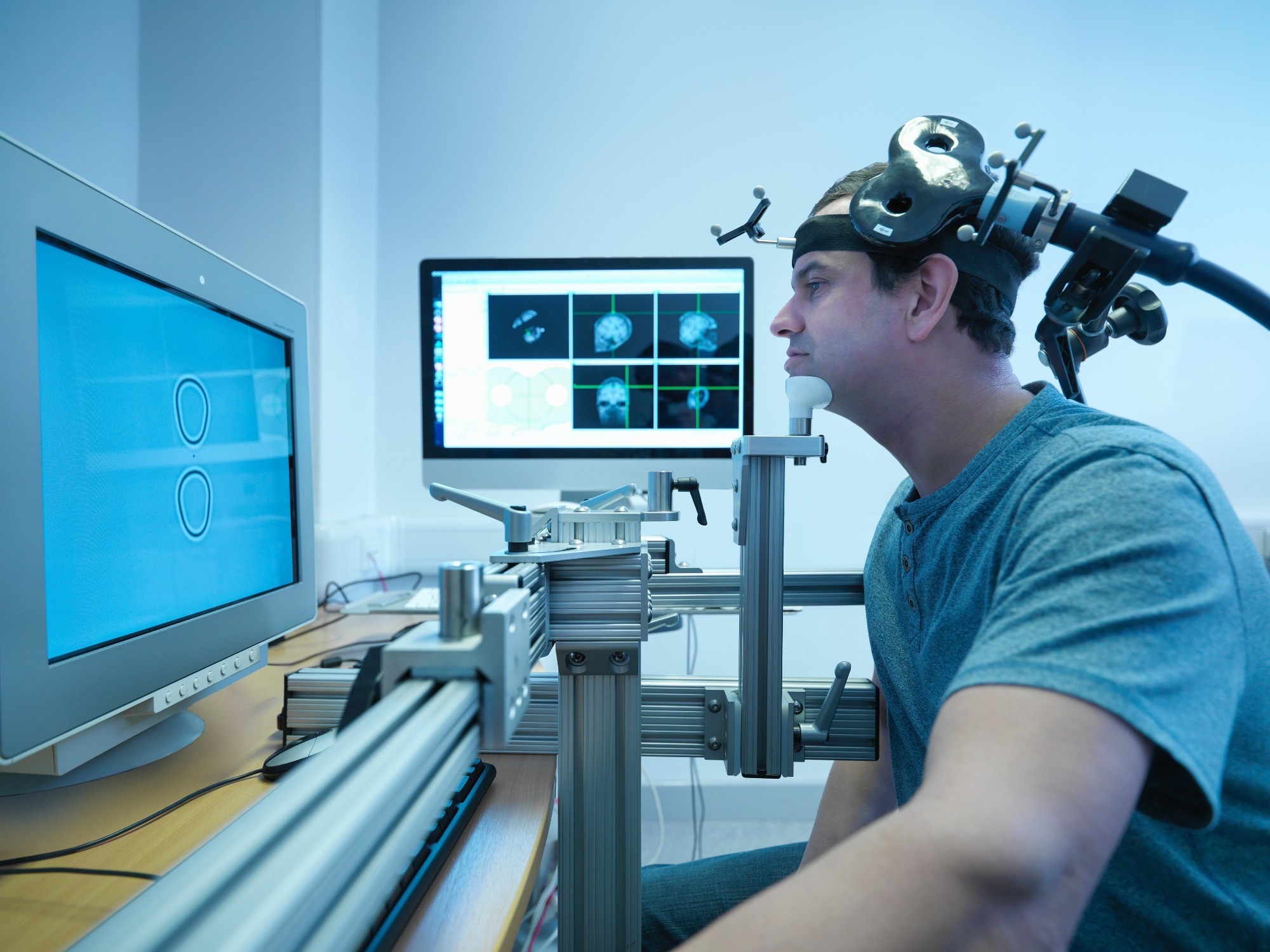
In a current research printed within the , a bunch of researchers evaluated the effectivity, therapeutic , and affected person perceptions of a customized robotic system for transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) coil placement in treating despair in comparison with conventional guide strategies.
Background
TMS is a non-invasive technique that makes use of magnetic fields to focus on mind neurons. Notably in treating despair with repetitive TMS (rTMS), it’s important to deal with particular mind areas, such because the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) which reveals lowered exercise in depressed sufferers.
Generally, the “5 cm rule” identifies this space, however neuronavigation supplies higher accuracy. The right coil placement is paramount for a number of causes, together with concentrating on, security, consistency, customization, and optimization of stimulation parameters.
Research have indicated that robotic TMS programs supply improved accuracy and lowered setup time in comparison with guide strategies. Regardless of considerations about potential accidents with robots, analysis on robotic TMS’s efficacy and affected person views is proscribed.
In regards to the research
Within the current research, a positioning robotic was designed for non-invasive mind stimulation to reinforce the accuracy and repeatability of the stimulation course of. Conventional industrial robots, as a consequence of their design, could be cumbersome when working across the human head.
In response, an revolutionary robotic rTMS mannequin was created, that includes a serial arm with a spherical mechanism. This design prioritized security and environment friendly motion across the mind. The superior model of this robotic had a wider workspace, bigger payload, and higher system stability, all tailor-made for exciting the prefrontal cortex.
This robotic mannequin retained its spherical mechanical benefits whereas that includes a broader workspace to accommodate a mean human head measurement and a heavier payload for the TMS coil and its cables.
To accommodate sufferers of various heights, a vertically adjustable stage was added, which was set as soon as the affected person was seated and remained fixed all through the remedy. Security mechanisms have been built-in, together with a braking system and a pressure or torque (FT) sensor, guaranteeing the robotic stopped if surprising occasions have been detected.
To command the robotic, an analytical answer was used, eliminating potential issues and constraining the robotic’s actions. The robotic’s movement was regulated at a frequency of 1 kHz, with an optical monitoring system working at 30 Hz.
On condition that sufferers would possibly transfer in the course of the 20-minute remedy, the robotic was designed to anticipate and modify to those actions, guaranteeing exact coil positioning.
Utilizing the robotic in rTMS remedy provided a number of benefits, together with extra correct and constant robot-assisted coil placement in comparison with guide positioning, and enhanced remedy repeatability as a result of saving of patient-specific goal positions by way of neuronavigation.
An included graphical consumer interface (GUI), together with neuronavigation, aided in pinpointing the stimulation website utilizing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) information. The affected person’s mind mannequin was generated by superior imaging methods, permitting clinicians to focus on the required cortical area precisely.
As soon as the robotic and the affected person’s head positions have been decided and visualized within the navigation system, the robotic might transfer on to the stimulation level after the preliminary remedy.
Additional, sufferers identified with main depressive dysfunction have been recruited, and out of the preliminary fifteen, fourteen have been assigned to both the robotic or guide rTMS group. The research adhered to moral pointers, and all individuals supplied knowledgeable consent.
Following preliminary evaluations, sufferers have been assigned to obtain both robotic or guide rTMS remedies over three weeks. The remedy parameters have been constant throughout each teams.
A set of imaging methods, together with MRI and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), have been used for evaluation earlier than and after remedy. The info was then statistically analyzed to find out the effectiveness and precision of each approaches.
Research outcomes
To grasp head motion throughout an rTMS session, researchers used a 3D measuring system to report the pose of the top. Whereas topics have been instructed to maintain their heads nonetheless, there was a gradual enhance in error over time, on condition that their necks weren’t mounted in place.
The crew designed two experiments evaluating guide and robot-assisted adjustment strategies. The primary experiment evaluated the precision and velocity with which the coil reached its goal area within the cortical space. Findings from this experiment revealed that the guide technique took virtually double the time because the robot-assisted technique.
This discrepancy is perhaps much more pronounced when contemplating two components: first, guide changes usually halted as soon as clinicians felt they might not enhance upon the present positioning error, which tended to be bigger than errors seen with robotic changes.
Second, the robotic’s velocity was deliberately slowed at sure factors to make sure affected person security. The research famous that the guide technique typically resulted in bigger errors than the robotic technique. The problem in controlling the coil manually, as each its place and orientation want simultaneous changes, is a major cause for these discrepancies.
Historic information from the crew’s prior analysis on ultrasound stimulation placement was referenced. In comparison with the TMS coil, the lighter ultrasound transducer was simpler to place manually, leading to accuracy surpassing the present experiment’s outcomes.
The research additionally examined the consistency of coil placement over time. Information confirmed that errors in guide positioning grew considerably inside simply 5 minutes, resulting in a shift of 9.81 mm from the unique placement after 10 minutes. In distinction, the robot-assisted technique showcased spectacular accuracy, ending with a ultimate place and orientation error of just one.43 mm and 0.32°.
Concerning demographic and scientific traits, no vital variations have been present in age, intercourse, or Beck Melancholy Stock (BDI-II). Following the rTMS remedy, a development towards decreased BDI scores was noticed within the robot-assisted group, whereas the guide group confirmed no such change.
Notably, adjustments in BDI scores between the 2 teams weren’t statistically vital. SPECT evaluation recommended a possible enhance in rCBF within the left DLPFC for the robot-assisted group, not seen within the guide group, however the between-group variations have been insignificant.
The research additionally utilized a questionnaire to know potential unwanted side effects when robots are utilized in remedy. This questionnaire assessed consolation, setup time, repeatability, depth, and security throughout robotic rTMS.
Curiously, regardless of the coil’s positioning being managed by a robotic, sufferers reported feeling protected and cozy. Nevertheless, some reported feeling the coil was not persistently positioned in the identical area, although the system was designed to keep up a constant error margin.
The crew hypothesized that sufferers may need unintentionally shifted the marker on their head, affecting the coil’s relative place. One other surprising discovering was that some sufferers felt various stimulation intensities throughout classes, which the researchers believed is perhaps as a consequence of sensory adaptation.